How Earnings Season Affects Stock Prices
Earnings season is a crucial period for investors and traders alike, often resulting in significant stock price movements. During this time, publicly traded companies release their quarterly financial results, which can either exceed or fall short of analysts' expectations. Understanding how earnings season affects stock prices requires looking at several key factors, including the relationship between earnings reports and stock price volatility, the role of analyst expectations, and the broader market sentiment.
The Role Of Earnings Reports In Stock Price Movement
The earnings report is a vital piece of information for investors, providing insights into a company's financial health, profitability, and growth prospects. These reports typically include key metrics such as revenue, net income, earnings per share (EPS), and guidance for future performance. When a company reports earnings that meet or surpass analysts' forecasts, it often leads to a surge in its stock price, reflecting positive sentiment among investors. Conversely, a report that misses expectations or reveals weaker-than-expected performance can cause a sharp decline in stock price.
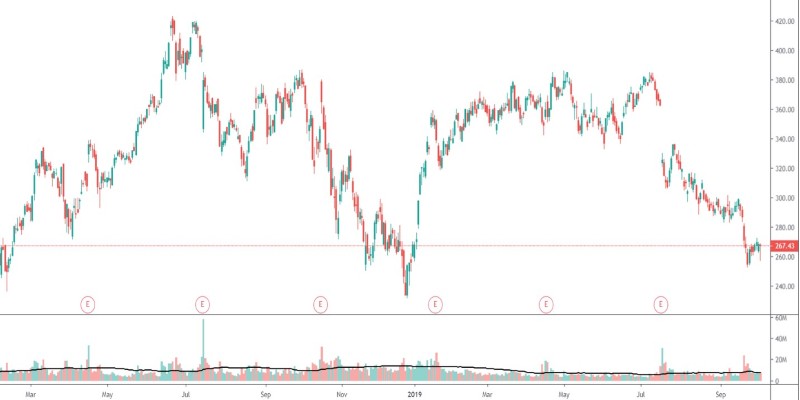
Earnings season is usually marked by high volatility, as stocks can experience significant price movements based on the results released by companies. The reaction to earnings reports is not just about the numbers themselves but also how those numbers compare to what analysts and investors had anticipated. If a company reports earnings significantly above or below expectations, it signals to the market that either the company's prospects are brighter than expected or more challenging than thought. This shift in expectations can directly affect investor behaviour, leading to buying or selling pressure that drives the stock price up or down.
Analyst Expectations And Stock Price Reactions
Before a company releases its earnings report, analysts provide earnings estimates, often based on trends, historical performance, and macroeconomic factors. These estimates set a benchmark that investors use to judge the company's performance. Suppose the reported earnings align with or exceed analyst expectations. In that case, it can generate a positive reaction in the stock market, as investors often interpret it as a sign of strong management and future growth potential.

On the other hand, if a company's earnings miss expectations, even if the numbers themselves are still positive, the stock price may suffer. This is because investors tend to react more strongly to earnings misses than to earnings beats, as a missed expectation can imply underlying problems or a future slowdown in growth. Even minor discrepancies between actual earnings and analyst forecasts can lead to significant market reactions, particularly when the market sentiment is already sensitive to macroeconomic conditions or industry-specific trends.
The broader economic environment can also influence the market's reaction to earnings results. During times of economic uncertainty, such as a recession or periods of high inflation, investors may be more cautious, and the stock price may be more sensitive to earnings misses. In contrast, in a strong economic environment, companies that report even modest earnings growth may experience significant price increases.
Market Sentiment And Its Impact On Stock Prices
Market sentiment plays a crucial role in determining how earnings reports affect stock prices. Sentiment is influenced by a variety of factors, including the overall state of the economy, geopolitical events, and the performance of other companies in the same sector. During earnings season, sentiment can drive the level of volatility in stock prices.
Positive sentiment, fueled by optimism about economic growth, technological advancements, or industry trends, can amplify the effect of a strong earnings report. Companies that report solid earnings in a buoyant market environment often see their stock prices rise more than they would in a neutral or negative sentiment environment. Conversely, negative sentiment, such as concerns over inflation, interest rates, or global instability, can dampen the effect of a positive earnings report, leading to smaller gains or even declines in stock prices despite good performance.
The Impact Of Forward Guidance On Stock Prices
In addition to reporting past performance, many companies provide forward guidance during earnings season. Forward guidance refers to management’s outlook for the upcoming quarter or fiscal year. This can include expectations for revenue growth, cost management, and other strategic initiatives that may impact the company’s performance.

Investors closely watch forward guidance as it provides insights into the company's prospects. A company that raises its guidance for future earnings is often rewarded with a rise in stock price, as investors interpret this as a sign of continued growth. Conversely, if a company lowers its guidance, it can lead to a drop in stock price, as investors may become concerned about the company's ability to meet future expectations.
Forward guidance is particularly important during earnings season because it offers a glimpse into the company’s strategy and future trajectory. However, it’s important to note that forward guidance can be subject to change, and companies may revise their outlook based on changing market conditions or unexpected events. Therefore, investors must carefully evaluate both the reported earnings and the forward guidance provided by the company to assess the stock’s potential.
The Psychological Effects Of Earnings Season On Investors
The psychological impact of earnings season cannot be overstated. For many investors, the release of earnings reports is a key event that shapes their view of a company's prospects. Earnings beats can create a sense of euphoria and confidence, encouraging investors to pile into a stock, thus pushing the price even higher. On the other hand, earnings misses can create panic, leading to mass sell-offs that drive stock prices down.

The volatility associated with earnings season can trigger emotions such as fear and greed, which often lead to short-term, reactive decision-making. This emotional response can exacerbate stock price movements, particularly in cases where the earnings results are unexpected or significantly deviate from analyst predictions. Some investors may even try to “time” the earnings season, buying stocks before earnings reports in anticipation of positive surprises or selling stocks ahead of earnings to avoid potential losses.
Conclusion:
Earnings season has a profound impact on stock prices, creating a dynamic environment where companies are held accountable for their performance and investors react to the financial results. The release of earnings reports, combined with analyst expectations, market sentiment, and forward guidance, can cause significant fluctuations in stock prices. These fluctuations can be driven by both rational evaluations of a company's performance and emotional reactions to the news.





